What are Health Disparities?
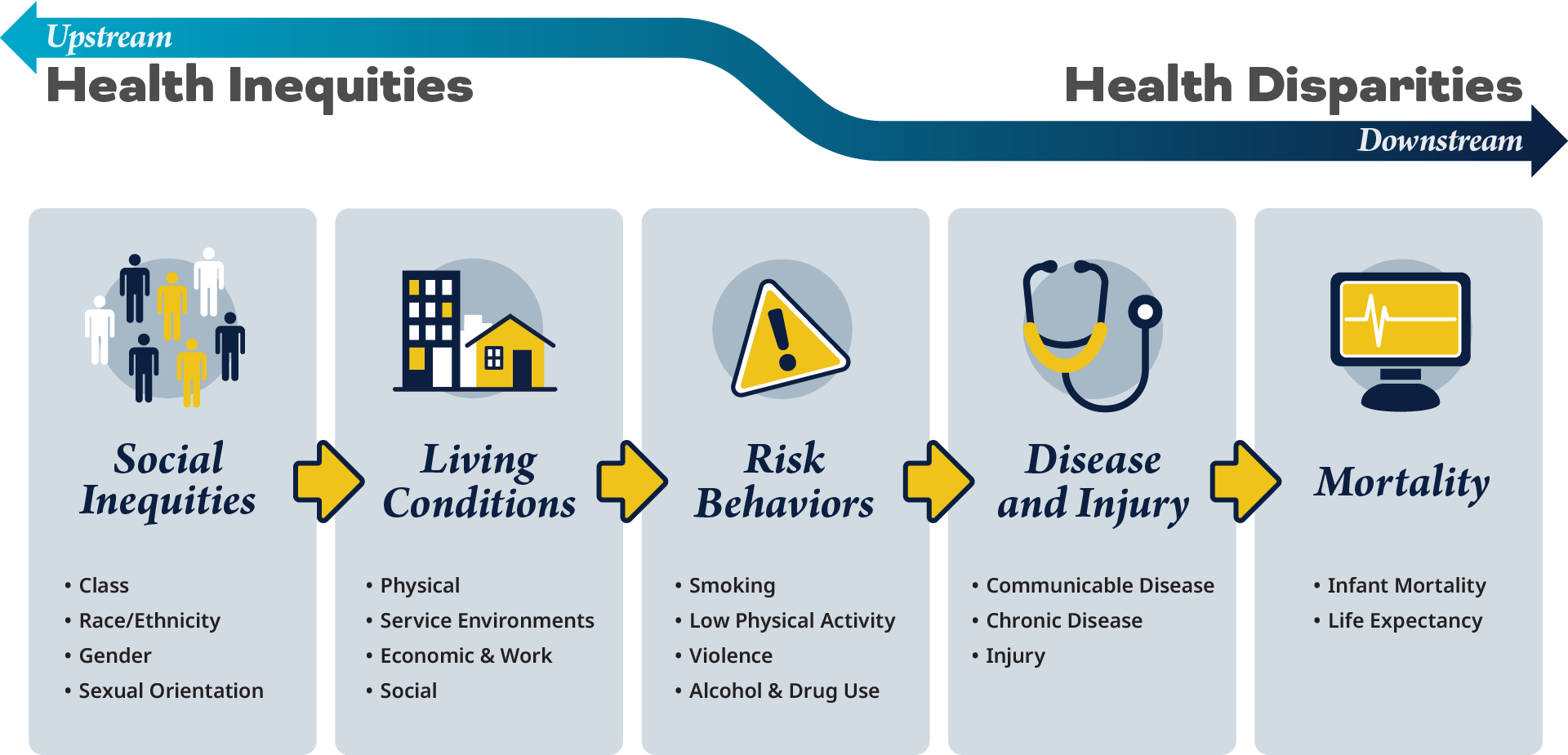
Picture a river. Imagine standing at two different points along its path: upstream, where the journey begins, and downstream, where the outcomes of that journey unfold. This imagery helps us understand the flow of factors that shape health inequities.
The Upstream and Downstream of Health
In public health, this concept serves as a framework. Upstream represents the root causes of health inequities—factors that shape our well-being from the start. These include socioeconomic status, race and ethnicity, access to quality education, housing, transportation, and health care, as well as the broader conditions in the places where people live, learn, work, and play. These are known as Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) and often create unequal opportunities for communities and individuals to achieve their best health.
Downstream refers to the outcomes influenced by these upstream factors. Health disparities manifest as differences in health outcomes between groups. For example, some communities experience higher rates of chronic illnesses, lower life expectancy, or barriers to accessing timely, quality care—highlighting the effects of these systemic inequities.
Why Recognizing Health Disparities Matters
Acknowledging the connection between upstream drivers and downstream outcomes is essential. It enables us to focus on addressing root causes and breaking down barriers to health equity. By identifying these inequities, we can develop strategies to create a more just and healthier society for all.
Join Us on the Journey Toward Health Equity
Together, we can advance initiatives that close health gaps, uplift underserved communities, and ensure that everyone has access to high-quality care. Explore our resources to learn more about how our organization is working to eliminate health disparities and how you can contribute to meaningful change. Let’s build a future where every person, regardless of their background, has the opportunity to thrive.

